Fueled by government infrastructure initiatives, oil and gas exploration, water projects, and increasing global demand, the Indian tube and pipe industry is entering a significant growth period, with stainless steel, carbon steel, and plastic pipes.
The concealed network of tubes and pipes supports all modern economies. Oil pipelines stretching across deserts and water supply systems reaching rural households rely on specialized tubes and pipes that serve industries as diverse as construction, energy, and transportation. The Indian tube and pipe industry is growing structurally, fueled by multi-sectoral demand, infrastructure spending, and government plans.
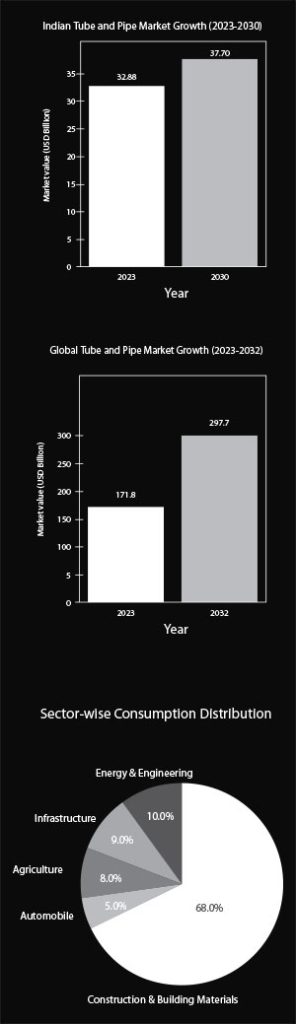
In 2023, the Indian tube and pipe market was worth USD 32.88 billion and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.43% until 2030, reaching almost USD 37.7 billion. Steel pipes command the market through established welded and seamless manufacturing capacity, while plastic alternatives gain traction in water infrastructure and residential construction projects.
The global tube and pipe market was worth USD 171.8 billion in 2023, and is expected to reach USD 297.7 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 6.3%. India’s manufacturing expansion and export capacity development align with this international growth trajectory, positioning domestic producers to capture increased market share while serving infrastructure projects that support broader economic development goals.
Current Market Landscape
The domestic tube and pipe industry caters to a broad spectrum of applications, including construction, oil and gas, water management, agriculture, automotive, and industrial engineering. Construction and building materials consume 68% of tube and pipe production, according to industry data, while energy and engineering applications account for 10% of demand. Infrastructure projects represent 9% of consumption, with agriculture at 8% and automotive manufacturing taking 5%.
Carbon steel pipes capture the largest market share through applications in oil and gas transmission, municipal water systems, and construction frameworks. Stainless steel variants target specialized sectors including chemical processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and power generation facilities where corrosion resistance proves essential.
Indian stainless steel seamless pipe production expanded 10.7% annually from 2019 to 2023, with manufacturers projecting 7.2% growth through 2027. This production increase reflects rising demand from domestic infrastructure projects and export opportunities in chemical processing equipment.
On the other hand, India’s plastic pipe market reached INR 55,000 crore in fiscal 2023 projecting growth to INR 1,30,000 crore by 2030, according to EY analysis. This 12% compound annual growth rate reflects infrastructure investment through government initiatives including the Jal Jeevan Mission and Smart Cities program.
PVC and OPVC pipes dominate water supply, sewage treatment, and irrigation applications due to corrosion resistance and reduced maintenance requirements compared to metal alternatives. Custom Market Insights forecasts the Indian PVC pipe segment will expand from USD 374.7 million in 2024 to USD 1.24 billion by 2033, representing 14.2% annual growth.
Urban expansion drives infrastructure upgrades across water distribution and sanitation systems. Manufacturing capacity increases target these requirements while government procurement contracts provide revenue visibility for established producers and new market entrants seeking to capture infrastructure spending.
Demand Drivers: A Multi-Sectoral Pull
The tube and pipe industry’s expansion rests on a stacked demand structure, where multiple sectors drive growth concurrently.
Construction and Urban Infrastructure
Construction alone accounts for nearly two-thirds of domestic pipe consumption. Rapid urbanization, which will push India’s urban population to 600 million by 2036, is fueling demand for pipes in housing, commercial complexes, and large-scale urban projects. Government initiatives such as PMAY (Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana), Smart Cities Mission, and AMRUT are generating large-scale orders for structural and plumbing pipes.
The Smart Cities Mission completed 8,000 projects worth INR 98,000 crore by its March 31, 2025 closure, with water supply, sewerage, and urban mobility infrastructure consuming substantial volumes of mild steel, ductile iron, and HDPE pipelines. These municipal contracts provided consistent revenue streams for domestic pipe manufacturers including Welspun Corp, APL Apollo Tubes, and Supreme Industries through multi-year project cycles.
AMRUT 2.0 approvals encompass 3,568 water supply projects valued at INR 1.14 lakh crore and 592 sewerage projects worth INR 67,608 crore. This government spending creates sustained demand for ductile iron pipe producers like Electrosteel Castings and polymer pipe manufacturers such as Finolex Industries and Prince Pipes through 2028.
PMAY-Urban’s extension to December 2025 maintains procurement schedules for last-mile plumbing systems and gas distribution networks in affordable housing developments. Tube manufacturers supplying residential construction expect order visibility through the program’s completion, supporting capacity utilization rates while municipal infrastructure projects transition to state-level funding mechanisms.
Metro projects in major cities like Delhi, Mumbai, Pune, and Bengaluru require significant volumes of steel pipes for structural purposes and plastic pipes for water and sewage systems. India’s operational metro rail network crossed 1,013 km as of May 27, 2025, with another 1,055 km under construction, keeping steel tubes/pipes demand elevated for viaduct utilities, station MEP, and depot networks.
Oil and Gas Transportation
India’s energy ambitions, including expanding its natural gas grid and enhancing LNG import terminals, are major demand drivers. Steel pipes, especially high-strength welded and seamless varieties, form the backbone of these transmission networks. Projects under the National Gas Grid and pipeline expansions by GAIL, IOCL, and ONGC are creating a sustained order book for manufacturers.
PNGRB has authorized 33,500 km of natural gas pipelines; about 25,000 km are already operational, driving steady demand for LSA-Welded SAW line pipes, bends and coatings. India’s crude oil pipeline network totals about 10,943 km (capacity 153.1 MMTPA) and product pipelines approximately 23,618 km (capacity 140.4 MMTPA), indicating a sizable, replacement-plus-brownfield market for API pipes and station piping.
Policy is reinforcing throughput: the government is targeting 15% natural gas share in the energy mix by 2030 (vs about 6.7% currently), with expansion of the National Gas Grid and CGD as core levers, both intensive in line pipe and city distribution networks (PE, steel).
The Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board (PNGRB) has so far authorized 307 geographical areas (GAs) under the City Gas Distribution (CGD) network. This expansion translates into the rollout of lakhs of kilometres of MDPE service pipelines alongside substantial steel interconnects, creating a robust urban gas infrastructure. Over the medium term, this buildout is expected to not only strengthen last-mile connectivity but also anchor broader urban utilities integration.
Water Supply and Sanitation
The Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) aims to provide piped water supply to 100% households, translating into a massive requirement for DI pipes, PVC/OPVC pipes, and steel pipes for trunk and distribution lines. This single program is estimated to boost demand for pipes by over 15% annually during its peak implementation years.
JJM now reports 15+ crore rural households with tap water (coverage 80%); over 2.63 lakh villages are certified ‘Har Ghar Jal’. The Centre is also considering extension till 2028, implying continued bulk DI/steel/PE pipe procurement for schemes and retrofits.
The Department of Drinking Water & Sanitation’s 2024-25 Annual Report pegs households getting tap water at 15.43 crore (as of Jan 22, 2025), with 12.19 crore connections added in five years, evidence of unprecedented execution scale benefiting DI and MS pipe producers. A six-year JJM review quantifies 12.45 crore connections delivered and overall 81% coverage, another confirmation of sustained DI/HDPE demand in rural transmission and distribution grids.
Industrial and Engineering Applications
Steel tubes are widely used in boilers, heat exchangers, and process industries, while stainless-steel seamless pipes find applications in chemical, petrochemical, and nuclear facilities, where corrosion resistance and high-pressure tolerance are critical. India’s crude steel capacity reached 198.5 MT (prov.) in FY25, with specialty steel output targeted at 42 MT by FY27 under the PLI scheme, supporting domestic availability of pipe grades, tubes for boilers/HRSGs, and process/structural applications.
Finished steel consumption growth remains robust; provisional Joint Plant Committee trends signal 7–10% demand growth in FY25, with DRI output leadership bolstering billet availability for ERW tubes. Trade policy is supportive: a 12% provisional safeguard tariff (April 2025) on select steel imports, largely targeting Chinese inflows, has already contributed to a 29% YoY drop in finished steel imports during Apr–Jun 2025, a challenge for domestic mills and downstream tube makers.
Agriculture
With agriculture consuming over 80% of India’s water resources, efficient irrigation systems are key to sustainability. Plastic pipes, especially uPVC and cPVC, are increasingly replacing conventional materials in irrigation and rural water supply projects, supported by government subsidies and modernization programs. Under PMKSY–PDMC (Per Drop More Crop), cumulative micro-irrigation coverage has reached 96.83 lakh ha (as of Aug 2025), driving steady demand for PVC/PE laterals, risers and GI/SS tube support systems.
The Cabinet cleared Modernization of Command Area Development & Water Management (M-CADWM) on Apr 9, 2025 to push underground pressurized piped networks from source to farm gate (upto 1 ha), with SCADA/IoT-enabled water accounting, direct upside for DI/MS/HDPE pipes and control valves. Meanwhile, NABARD’s Micro-Irrigation Fund notes 21.69 lakh ha covered by states (to Mar 31, 2025), signaling a continuing pipeline (pun intended) of district-level tenders for buried mains/sub-mains and on-farm distribution.
Automotive Sector
Automotive applications, though smaller in share, demand precision tubes for fuel lines, shock absorbers, and structural components, a niche but high-value segment that is growing with the push for electric vehicles and lightweighting. In fiscal 2025, with total vehicle production reaching 31.03 million units. Passenger vehicle sales hit 4.30 million units while commercial vehicle output reached 960,000 units, sustaining demand for electric resistance welded and drawn-over-mandrel tubes in chassis construction and body-in-white applications.
Two-wheeler production of 19.61 million units drove consumption of lightweight tubes for exhaust systems and frame construction as manufacturers including Hero MotoCorp and Bajaj Auto adopted thinner-wall specifications to reduce vehicle weight. Electric vehicle adoption creates additional demand for specialized aluminum and steel tubes rated for battery cooling systems and structural protection.
Vehicle exports rose 19% to 5.36 million units in fiscal 2025, tightening delivery schedules for tube suppliers. This export growth maintains capacity utilization at precision tube manufacturers despite mixed monthly production data in early fiscal 2026.
Tube manufacturers targeting automotive applications command higher margins than commodity producers serving construction markets. Electric vehicle transition requires investment in aluminum processing capabilities and precision welding equipment to meet lightweighting requirements from original equipment manufacturers.
Policy Push & Government Initiatives
Government policies have acted as powerful enablers for the growth of the tube and pipe sector. The Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for Specialty Steel encourages the production of high-grade steel, thereby reducing import dependence. Similarly, the Domestically Manufactured Iron & Steel Products (DMI&SP) Policy promotes the use of indigenous steel in government projects, boosting domestic demand.
The National Infrastructure Pipeline, with an allocation of INR 11.21 lakh crore for FY2025-26, including INR 1.16 lakh crore earmarked for roads and bridges, is expected to significantly drive demand for structural and drainage pipes. Complementing this, the PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan is improving logistics and connectivity, thereby facilitating the execution of large-scale pipeline projects. Additionally, the implementation of Quality Control Orders, mandating BIS compliance for both steel and plastic pipes, ensures standardized quality and safety across the sector.
Export Potential: Tapping Global Opportunities
While the domestic market remains the primary growth engine, export opportunities are expanding, particularly in oil & gas, water transmission, and specialty stainless-steel segments.
The global tube and pipe market, projected to reach USD 297 billion by 2032, presents a huge opportunity for India. Welspun Corp, Surya Roshni, and Jindal Stainless are already significant exporters to GCC nations, North America, and Europe.
Global supply chain diversification under the China+1 strategy is beginning to benefit Indian manufacturers. Although India’s current share is modest compared to China’s dominance, its cost competitiveness, compliance with API/BIS standards, and growing capacity position it as a credible alternative for international buyers in oil & gas and infrastructure segments.

Technology, Sustainability, and Innovation
Modern tube and pipe manufacturing has evolved well beyond conventional commodity steel, embracing advanced technologies and sustainable practices. For instance, state-of-the-art high-end coatings are being routinely applied to steel used in oil and gas pipelines to significantly enhance corrosion resistance and extend service life, an increasingly critical feature given the aggressive environments these pipelines often traverse. In parallel, innovations in seamless pipe technology are enabling their use in demanding high-pressure applications, where traditional welded pipes may fall short.
On the plastic side, the evolution of OPVC (modified PVC) and related plastic pipe technologies is gaining momentum. The Indian PVC pipes market alone reached 2.9 million tonnes in 2024, and is projected to more than double to 5.5 million tonnes by 2033, growing at a robust CAGR of 6.8%. Broader estimates of the Indian plastic pipe market, including PE, PP, and other types, suggest it will reach around USD 9 billion by 2030, expanding at a steady 5% CAGR from 2024 to 2030.
Beyond volume growth, Indian manufacturers are increasingly adopting advanced extrusion technologies, such as twin-screw extruders, energy-efficient heating systems, in-line quality control tools, and automation with AI-based monitoring, to ensure precision, reduce downtime, and scale production while maintaining quality standards.
On the sustainability front, there’s a growing shift toward greener steelmaking practices. Although challenges remain, such as the fact that only about 21% of India’s steel production currently comes from scrap-based (electric arc furnace) routes, the potential is significant. Scrap-based processes substantially lower carbon emissions and energy consumption, especially when combined with renewable electricity. While traditional coal-based blast furnaces remain predominant, greener alternatives like electric arc furnaces (EAFs) are gaining ground as low-emission options. Moreover, emerging innovations such as hydrogen-based direct reduced iron (DRI) and the HIsarna process (demonstrated by Tata Steel to reduce CO₂ emissions by more than 50% without carbon capture) are being explored for their efficiency and environmental advantages.
Energy efficiency is another cornerstone. Many steel producers are transitioning to energy-efficient furnaces and adopting zero-liquid-discharge practices to minimize environmental impact and conserve water, key considerations for sustainable manufacturing. Although precise figures for these practices in the Indian tube and pipe sub-sector are harder to isolate, they align with broader industrial shifts toward greener operations across the steel and plastic value chains
Performance & Strategy of Leading Companies
The Indian tube and pipe sector is strongly supported by some of the country’s largest steel producers and specialized pipe manufacturers, whose financial strength and strategic investments continue to drive growth and competitiveness. Leading pipe manufacturers reported fiscal 2025 financial results that illustrate the sector’s revenue scale and growth trajectory across steel, plastic, and specialty segments. Coverage constraints limit analysis to only a handful of companies, though many other producers and specialty fabricators contribute significantly to India’s tube and pipe manufacturing capacity.

Tata Steel, with revenues of INR 2,18,543 crore and a profit of INR 3,174 crore in FY25 (profit turnaround of 165% YoY), remains the largest player in the domestic steel ecosystem. Its Tubes Division crossed the milestone of 1 million tonnes in both production and sales, consolidating its leadership in structural and conveyance tubes. The company is also investing heavily in green-steel technologies, including electric arc furnaces and pilot projects in hydrogen-based reduction, positioning itself as a global frontrunner in sustainable steelmaking. Tata Steel India, the core operating unit, reported revenues of INR 1,33,444 crore (up 6.6% YoY) and profits of INR 13,803 crore (up 6.1% YoY), and continues to focus on high-value tube products and supply-chain integration for downstream industries.
Steel Authority of India Limited (SAIL), with a turnover of INR 1,01,716 crore and profits of INR 2,148 crore, plays a pivotal role as a domestic supplier of crude steel, feeding into the pipe manufacturing ecosystem. Its modernization and capacity expansion plans, particularly at Bhilai and Bokaro, strengthen its ability to meet the growing demand for pipes used in infrastructure, energy, and construction projects.
Among stainless-steel producers, Jindal Stainless (JSL) has emerged as a global force. With revenues of about INR 40,182 crore (up 5%) and profits of INR 2,711 crore (up 7% YoY), it is India’s largest stainless-steel producer and among the top five globally. The company is expanding stainless steel pipe capacities and targeting a stronger export footprint, building on its already significant presence across more than 40 countries.
APL Apollo Tubes, India’s leading structural steel-tube manufacturer, reported revenues of INR 20,690 crore (up 13.7% YoY) and profits of INR 757 crore (up 3.4% YoY) in FY25. With an installed capacity of 4.5 MTPA and plans to expand towards 6.8 MTPA by FY28, APL Apollo has positioned itself as a key enabler of India’s infrastructure boom. Its product mix, spanning structural, construction, and agricultural applications, underscores its diversified strategy.
Welspun Corp remains a major player in welded pipes, with revenues of INR 13,978 crore and EBITDA of INR 1,858 crore (up 3% YoY). The company has been aggressive in expanding ductile iron pipe capacities and continues to strengthen its global footprint, supported by a healthy order book and ongoing capex exceeding INR 900 crore. Welspun’s international arm, Welspun Pipes Inc. (USA), together with its holdings in Welspun Tubular LLC and Welspun Global Trade LLC, reported consolidated revenues of INR 2,442 crore and a profit of INR 101 crore in FY25, reflecting its continued role as a material foreign subsidiary. On the domestic front, Welspun DI Pipes Ltd. delivered robust growth with revenues of INR 2,062 crore (up 36% YoY) and profits of INR 292 crore (up 186% YoY), attaining the status of a material subsidiary under SEBI regulations. Additionally, Welspun Corp holds a 26.5% stake in East Pipes Integrated Company for Industry (EPIC), a Saudi Arabian associate that reported revenues of INR 4,141 crore (up 22% YoY) and profits of INR 863 crore (up 46% YoY). EPIC supplies advanced HSAW pipes, certified up to API 5L X-80 grades, to major clients such as SWCC and Saudi Aramco, further reinforcing Welspun’s global leadership in the pipes industry.
In the mid-sized category, Surya Roshni reported revenues of INR 5,749 crore and EBITDA of INR 446 crore (up 2.3% YoY). With state-of-the-art facilities across Haryana, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and Andhra Pradesh, the company is executing a INR 500 crore capex plan over two years to increase pipe capacity from 1.2 MTPA to 1.9 MTPA. This includes raising investment at its Hindupur facility from INR 75 crore to INR 125 crore, adding 2,00,000 TPA capacity, and a INR 75 crore investment at Bhuj (Anjar) for large diameter pipes. It has also commissioned a new spiral plant in Gwalior in February 2025 and is expanding cold rolling capacity at Bahadurgarh by H1FY26. Products marketed under the ‘Prakash Surya’ brand are exported to over 50 countries, including a strong presence in GCC markets, while domestically, Surya maintains a wide B2C presence, particularly in Tier II cities and rural regions through its dealer-distributor network.
In this category, Maharashtra Seamless Limited (MSL), with revenues of INR 5,266 crore and profits of INR 793 crore, continues to dominate the seamless pipe market, catering to oil & gas and engineering sectors while pursuing export opportunities despite margin pressures. Ratnamani Metals & Tubes, with revenues of INR 4,959 crore and profits of INR 579 crore, is distinguished by its high export orientation and technical leadership, including the supply of hydrogen-service-compliant pipes for global energy projects.
Goodluck India, with revenues of INR 3,936 crore (up 11.7% YoY) and profits of INR 162 crore (up 23.9% YoY), has diversified into value-added tubes, including a new hydraulic tube facility with 50,000 tonnes annual capacity, aimed at sectors such as railways, defence, and automotive. Hi-Tech Pipes posted revenues of INR 3,068 crore (up 13.6% YoY) and profits of INR 73 crore (up 66% YoY), supported by double-digit volume growth and a strategy focused on infrastructure and agriculture demand. JTL Industries, with revenues of INR 1,916 crore and profits of INR 99 crore, is scaling up its structural tube capacity while concentrating on margin expansion through value-added product lines.
Among the emerging players, Sambhv Steel Tubes reported revenues of INR 1,511 crore (up 17.5% YoY) and profits of about INR 57 crore. Having recently launched an IPO to raise capital for expansion, the company reflects the dynamism of smaller, fast-growing firms consolidating their position in India’s highly competitive pipe and tube sector.
Collectively, these companies demonstrate a robust blend of financial resilience, capacity expansion, technological innovation, and sustainability focus. Their strategies, from Tata Steel’s net-zero roadmaps to Ratnamani’s hydrogen-ready pipelines and Surya Roshni’s export-led growth, highlight how India’s tube and pipe industry is aligning with both national infrastructure priorities and global energy transitions.
Challenges
Despite its rapid expansion, the Indian tube and pipe industry continues to contend with multiple challenges that affect margins and long-term sustainability.
Raw Material Price Volatility (Steel and PVC Resins)
Steel and PVC are the primary raw materials for the tube and pipe industry, and their prices remain highly volatile due to fluctuations in global commodity markets, energy prices, and trade policies. For instance, Surya Roshni noted that sharp swings in hot-rolled coil (HRC) steel prices directly impact margins in its ERW and structural pipe business. Similarly, volatility in crude oil derivatives drives cost fluctuations in PVC resins, putting pressure on profitability in the polymer pipe segment. This uncertainty compels companies to either absorb higher costs, reducing margins, or pass them on to customers, which risks demand slowdown.
Import Pressure from Low-Cost Markets
Indian pipe manufacturers face stiff competition from imports, particularly from countries like China, Vietnam, and Middle Eastern producers, where production costs are lower. Reports highlight that Indian companies, despite investing in capacity and advanced technologies such as Direct Forming Technology (DFT) and 3LPE coating facilities, are often undercut by cheaper imports. This pressure intensifies in segments like API-grade pipes and structural tubes used in infrastructure projects, eroding domestic players’ pricing power.
Logistics Bottlenecks Affecting Timely Deliveries
Transportation delays, high freight costs, and port congestion remain bottlenecks for both domestic and export markets. For export-focused players such as Surya Roshni, one of the largest Indian exporters of ERW pipes, timely shipments to over 50 countries are often challenged by shipping line shortages, rising container costs, and infrastructure gaps in last-mile connectivity. Domestically, rail and road bottlenecks lead to higher lead times and costs, which affect order execution schedules for large-scale infrastructure and oil & gas projects.
Compliance Costs for BIS and International Standards
Pipe and tube manufacturers in India must adhere to stringent BIS specifications as well as API and ISO certifications for international sales. While these standards enhance product credibility, the associated compliance and testing requirements raise operational costs. Companies frequently invest in advanced testing, coating, and R&D facilities to remain compliant, but the burden is heavier for mid-sized players who operate on thinner margins. Surya Roshni, for example, invested in state-of-the-art coating and quality-testing facilities to meet international project consultancy accreditations (like EIL and Mecon). However, continuous upgrades and audits add to recurring compliance expenditure.
Future Outlook
The Indian tube and pipe industry is poised to evolve from being a volume-driven sector to one that increasingly competes on technology, sustainability, and value-added solutions. Beyond the expected 6–7% annual growth, the next phase will be marked by greater product specialization, including precision-engineered hollow sections for infrastructure, higher-grade stainless steel for process industries, and advanced coatings for longer service life in demanding environments.
Digitalization and automation are set to reshape manufacturing processes, with leading companies deploying smart quality-control systems, AI-based demand forecasting, and end-to-end supply chain integration. These capabilities will not only reduce costs but also improve reliability and responsiveness, which are critical in global markets.
Sustainability will emerge as both a challenge and an opportunity. As customers across oil & gas, water utilities, and infrastructure increasingly mandate lower carbon footprints, Indian manufacturers are expected to invest in green steel, energy-efficient production lines, and circular material usage. Firms that embed ESG compliance early will gain a distinct advantage in global tenders and long-term contracts.
The industry is also likely to witness consolidation, with larger players expanding capacity, acquiring regional competitors, and diversifying into adjacent product categories such as structural tubes, PVC fittings, and composites. Access to capital, both domestic and international, will play a critical role, as companies with stronger balance sheets can accelerate expansion and R&D investments.
On the global front, India is well positioned to capture a larger share of the tube and pipe supply chain as Western economies diversify sourcing beyond China. Securing certifications such as API, ASTM, and PED will remain essential, but equally important will be building long-term partnerships with EPC contractors, utilities, and energy companies.
In essence, the industry’s trajectory will be defined by rising demand and how effectively it aligns with global megatrends: sustainability, digital manufacturing, supply chain resilience, and strategic consolidation. Companies that adapt to these shifts will shape India’s transition from a cost-competitive supplier to a global hub for high-quality, future-ready tube and pipe solutions.
Also Read: Jindal Industries Hissar Coming Up with New 1.5 Million TPA Facility at Hansi
Role of B2B Exhibitions: Tube & Pipe Fair
Against the backdrop of sustained demand and rising export ambitions, B2B exhibitions occupy a distinctive position in the industry’s growth ecosystem. They condense the extended timelines of market outreach and trust-building into a concentrated, face-to-face exchange. For tube and pipe manufacturers, this setting allows for direct demonstration of product performance, on-the-spot validation of quality, and detailed technical discussions with institutional buyers, all within a compressed timeframe that accelerates decision-making.
Launched by Tulip 3P Media in 2023, the Tube & Pipe Fair (TPF) has quickly emerged as South Asia’s largest dedicated platform for the sector. The inaugural edition at Delhi’s Pragati Maidan (October 2023), co-located with Cable & Wire Fair (CWF), attracted over 3,000 visitors and more than 70 leading brands, offering a glimpse into the latest technologies and product innovations. Encouraged by its success, the organizers expanded the footprint to Hyderabad’s HITEX Centre in August 2024. With participation crossing 100 brands and footfall rising to 5,000, supported by greater involvement of both domestic and international technology providers, the southern sojourn proved to be a success.
Building on this momentum, the third edition of TPF is scheduled to return to New Delhi’s Pragati Maidan from 4th to 6th November 2025. Its co-location with the Cable & Wire Fair and the inaugural Bharat Metal Expo (BME) reflects the increasing interdependence of the industries it serves, with cables, tubes, and metals forming the material backbone of energy, transport, and manufacturing systems. This convergence creates opportunities for buyers and suppliers to address interconnected procurement needs in a single venue, while also enabling cross-sector technology transfer.
Evidence from previous editions points to tangible commercial outcomes. Exhibitor surveys indicate that over 40 percent of participants secured confirmed orders during the event, while more than 30 percent of leads generated translated into business within the following year. For smaller and mid-tier companies, the fair offers cost-effective access to national and export markets; for larger players, it has become a strategic point for launching new products, reinforcing brand leadership, and, in some cases, pre-booking production slots for high-demand items months in advance. International buyers often use the event to assess Indian suppliers first-hand, a step that can lead to long-term contracts or joint ventures, particularly in markets such as Europe, the Middle East, and North America.
Beyond the transactional dimension, TPF along with BME serves as a setting for sector-wide dialogue on technology, regulation, and market direction for tube and metal industries. Its conferences and technical sessions have addressed issues ranging from evolving BIS norms and export compliance requirements to innovations in conductor and insulation technology. The introduction of new machinery, materials, and testing protocols at the fair has often accelerated the industry’s adoption of best practices, whether in extrusion line upgrades or enhanced fire safety measures.
As the sector enters a phase of consolidation and deeper integration with global supply chains, forums like the Tube & Pipe Fair provide more than visibility; they function as mechanisms for aligning domestic capabilities with international benchmarks. In doing so, they help ensure that the industry’s projected growth is matched by parallel advances in quality, innovation, and competitiveness.